how to make a 3d model
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take reward of the latest features, security updates, and technical back up.
Employ Blender to prepare 3D models for use in Dynamics 365 Guides and in mixed-reality components included in apps created with Power Apps
This tutorial provides step-by-pace instructions that show you how to:
-
Reduce the polygon count of a 3D model so that it matches the operation needs specific to operation targets for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Guides and for mixed-reality components included in apps created with Microsoft Power Apps.
-
Combine the 3D model'due south multiple materials (colors) into a single texture that can be practical to the model.
-
Export the optimized 3D model every bit a GLB file that can be used in Dynamics 365 Guides and Ability Apps.
The combination of reducing polygons and turning multiple materials into a unmarried texture tin can transform a circuitous and resource-intensive 3D model into a 3D model that performs well in Dynamics 365 Guides and Power Apps.
Important
This document is created strictly for informative purposes to demonstrate how Blender works with Dynamics 365 Guides and Power Apps. Your use of third-party applications is field of study to terms between yous and the tertiary party. Microsoft Corporation is not affiliated with, is non a partner to, and does not endorse or sponsor Blender or any of Blender's products. There are other content-creation apps you can use to prepare your 3D models.
What is Blender?
Blender is a free, open-source 3D creation suite. It supports the entirety of the 3D pipeline: modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing and movement tracking, and video editing and game cosmos.
If Blender is the software that you decide to utilize to prepare your 3D models, review Blender's website and download the most current stable version for Windows.
Overall steps for preparing a 3D model with Blender
Preparing a 3D model for mixed reality with Blender includes the following steps:
-
Import the model into Blender.
-
Decimate the model.
-
Unwrap the model (UV unwrapping).
-
Assign materials.
-
Bake the textures.
-
Export the model as a GLB file.
Import the model into Blender
-
Open up Blender. When yous open the app, a new scene is automatically created.
-
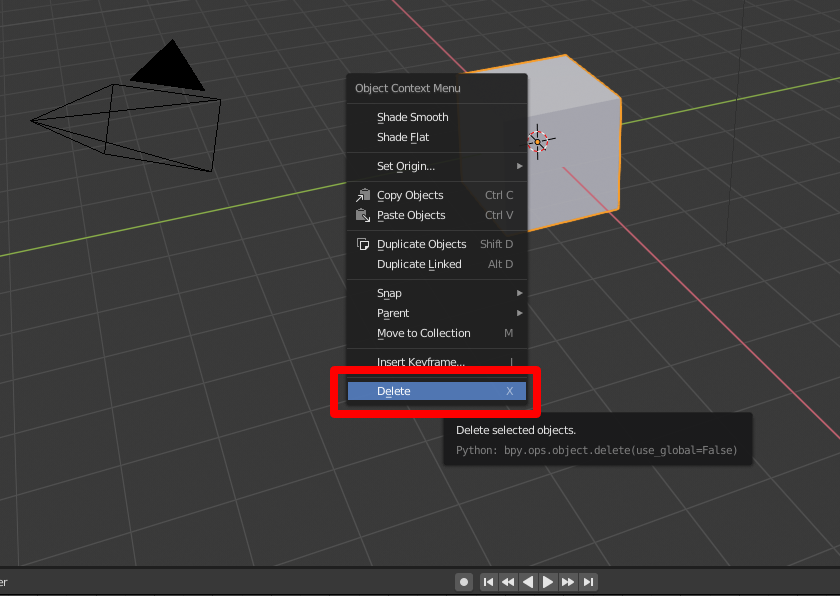
Right-click the cube, and and so select Delete to delete it.
-
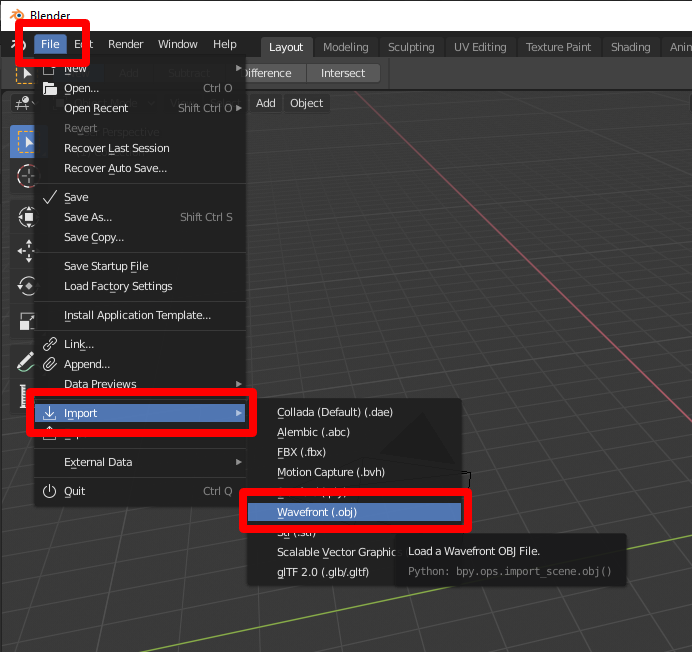
Select File > Import > Wavefront (.obj) to import the OBJ file.
-
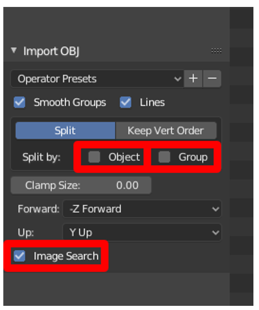
Under Import OBJ, do the following:
a. Clear the Object and Group cheque boxes, and select the Image Search bank check box.
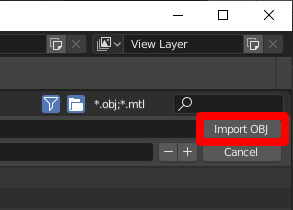
b. Select Import OBJ on the right side of the screen. This imports the 3D model as one item, and searches in the subfolder for any materials.
When you select Import OBJ, you lot'll see the 3D model with the imported materials.
Tip
If the 3D model is extremely large or pocket-sized, or hard to see, or is mayhap off-screen as shown in the post-obit graphic, yous can employ the mouse bike to zoom the camera in or out until the model is visible.
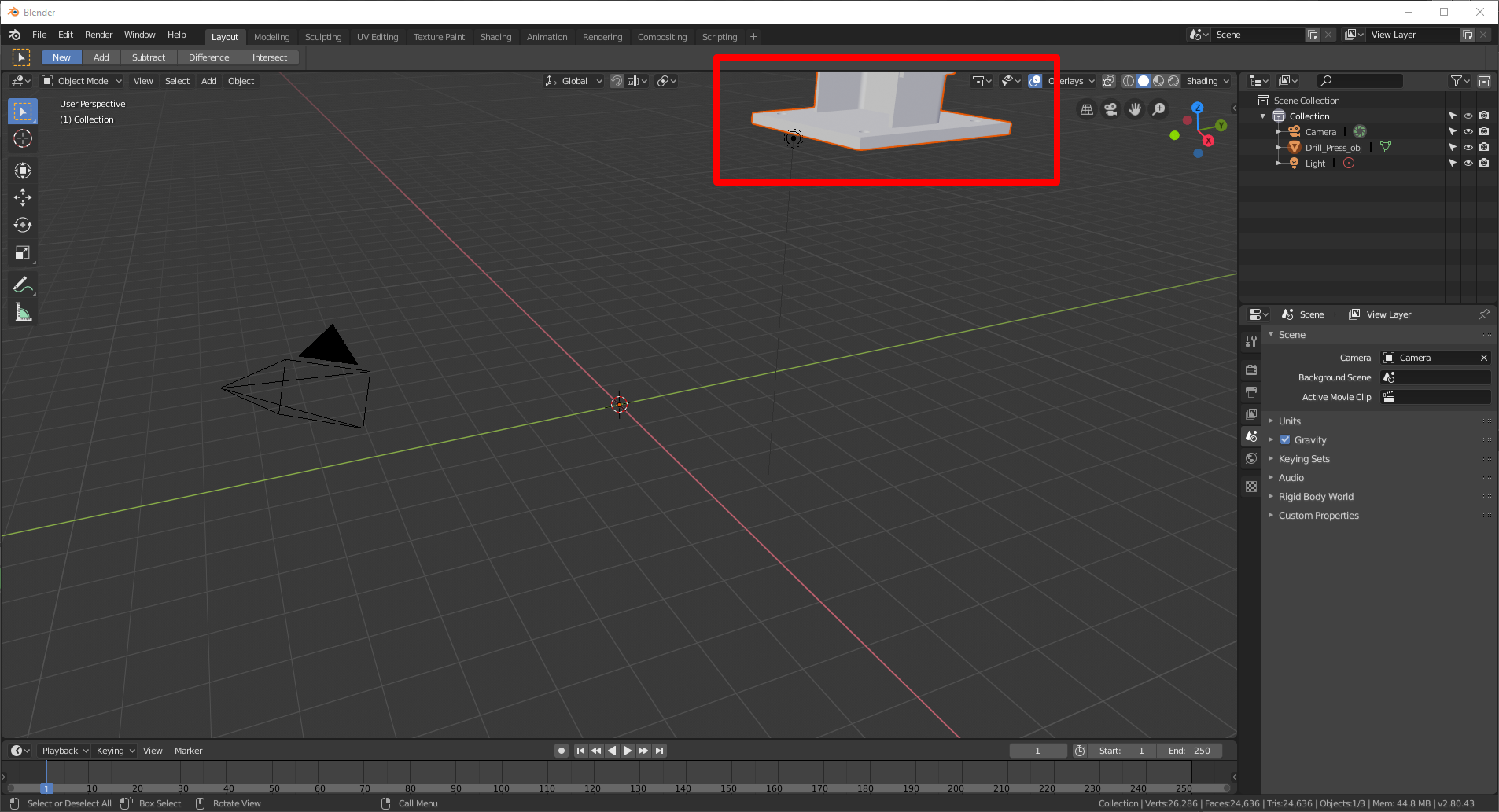
If the 3D model appears gray, select the Look Dev shading choice to prove the colors.
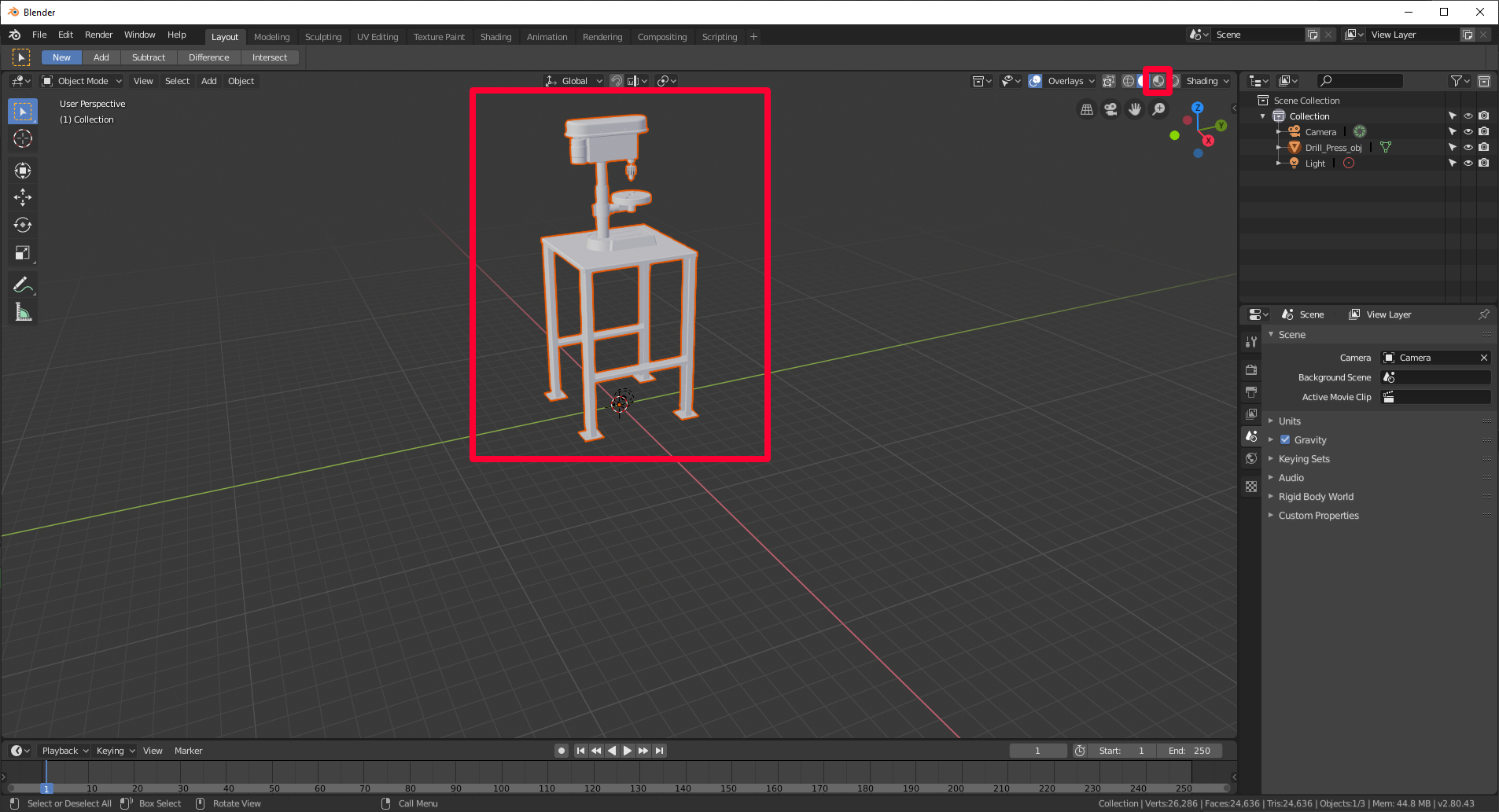
c. Review the Tris count (number of polygons) at the bottom correct of the screen.
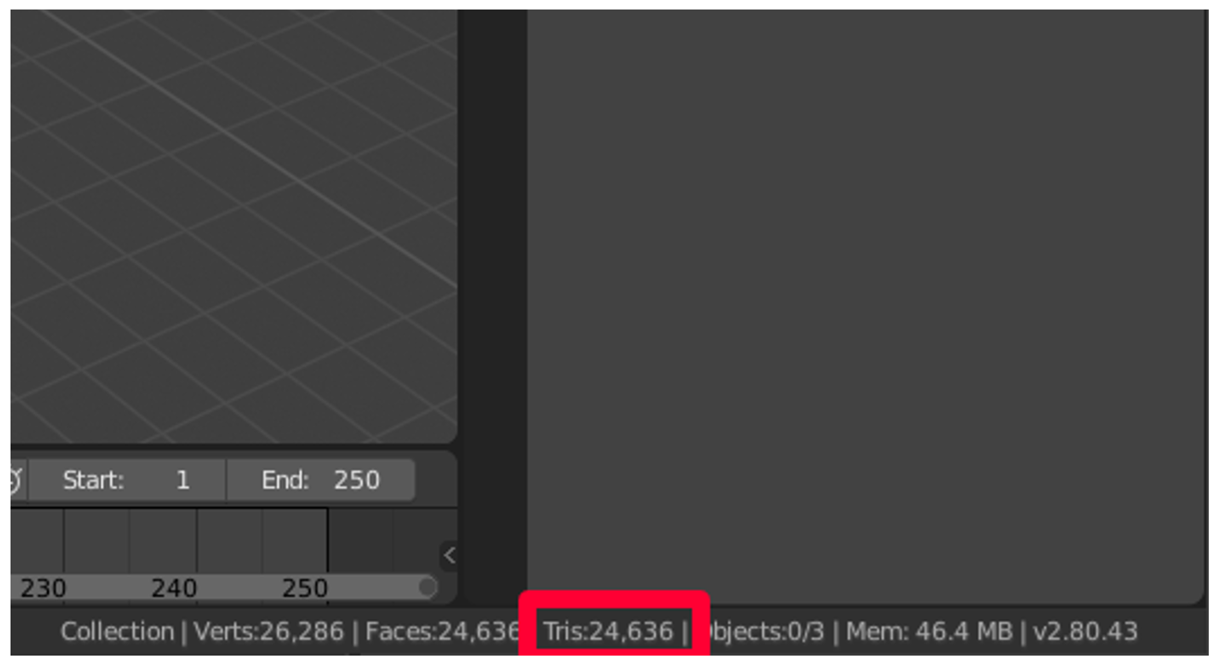
If this number meets the performance target resolution, yous can skip the decimation pace and become directly to Unwrap the model later on in this tutorial. If it doesn't meet the target resolution, keep to the next department to decimate the model.
Decimate the model
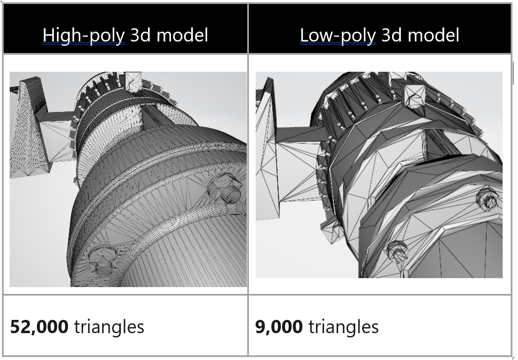
To achieve application-specific functioning goals, you lot might demand to "decimate" the model. Decimation is the process of recomputing the surface polygons of the model to create a similar shape with fewer polygons. This reduces visual fidelity, but increases functioning. The example images below testify a high-allegiance model that can be used when y'all're viewing one or 2 3D models at a time on Microsoft HoloLens, and a depression-quality 3D model used when you're viewing ten or more models at a time on HoloLens.
-
Select the model, and then go to the Modifiers card
 in the tool column on the right.
in the tool column on the right. -
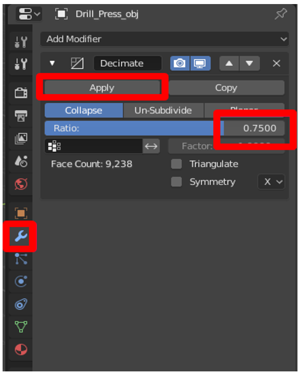
On the Modifiers menu, in the Add Modifier list, select Decimate.

-
With the model selected, change the Ratio value to a number between 0.0 and 1.0. This setting determines the percentage of polygons (triangles) that are removed. For example, a value of 0.5 reduces the original polygon count to 50%. You'll meet the Tris value in the bottom correct of the Blender window decrease as you change the ratio. When the number reaches a value that matches your functioning goal and looks good, select Apply.
Unwrap the model (UV unwrapping)
You can skip this step if your model has just 1 color.
To visualize the concept of UV unwrapping, imagine cutting out every surface of a 3D model and placing those surfaces flat on a piece of paper. The U and Five dimensions represent the vertical and horizontal axes of the piece of paper in the aforementioned way that 10, Y, and Z represent the three-dimensional axes of a 3D model. Unwrapping the UVs enables you lot to pigment the flattened pieces with the material colors of the model. This painted paper is called a texture, and it'south subsequently wrapped back on meridian of the model, giving information technology the illusion of being made from different-colored pieces when information technology'southward really one item with a colorful texture wrapped around it. This procedure is chosen texture baking, which is covered later in this tutorial.
-
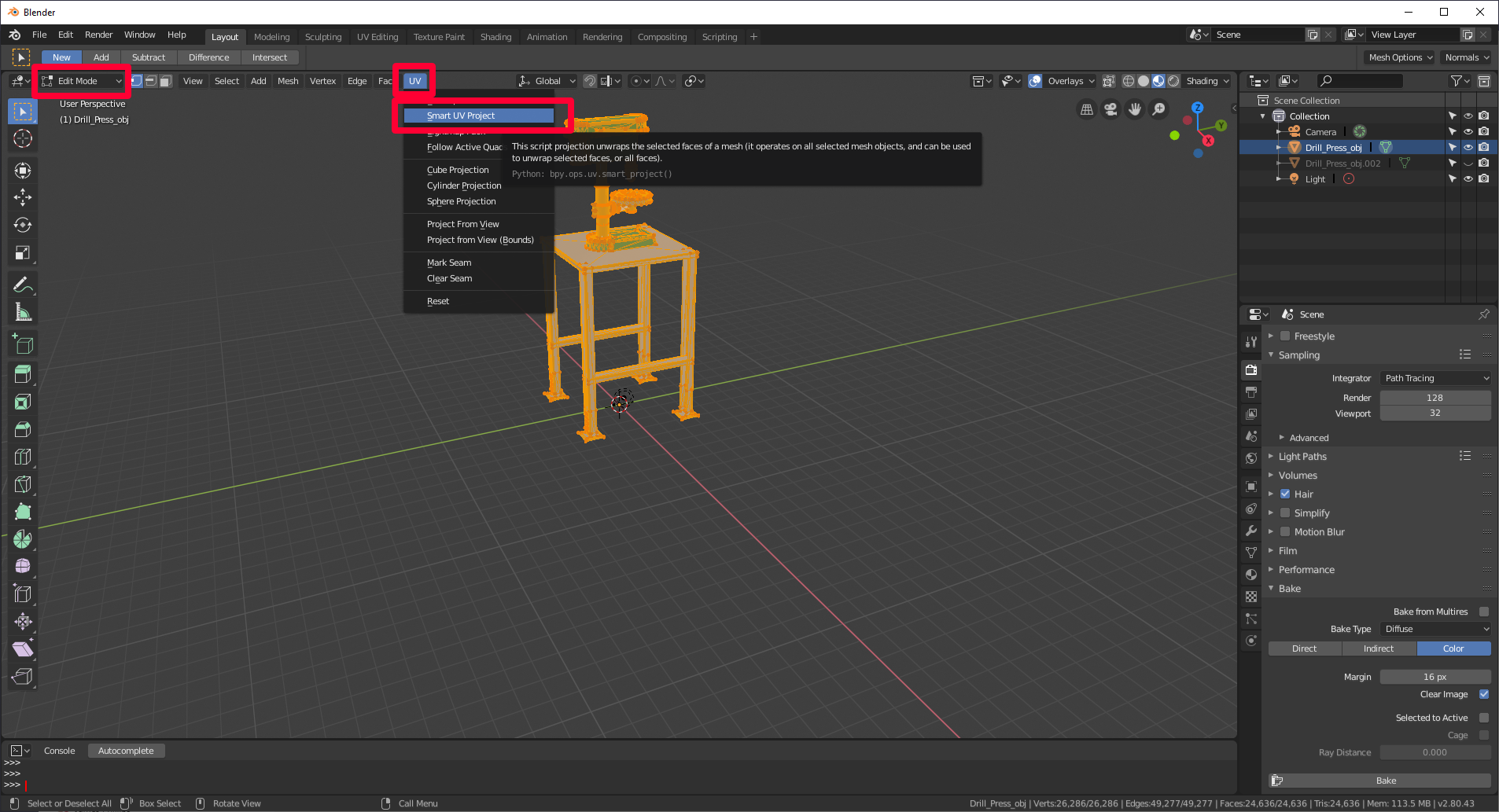
Select the model, hover over the primary carte, printing the Tab fundamental to enter Edit Mode, press a to select all, and then on the UV carte du jour, select Smart UV Project.
Tip
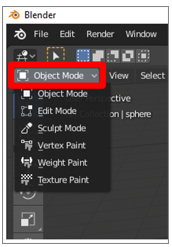
Enter Edit Mode by selecting the Edit Way listing in the upper-left corner, or press the Tab central. Pressing the Tab key while already in Edit Mode returns you to Object Mode, as shown in the following graphic.
-
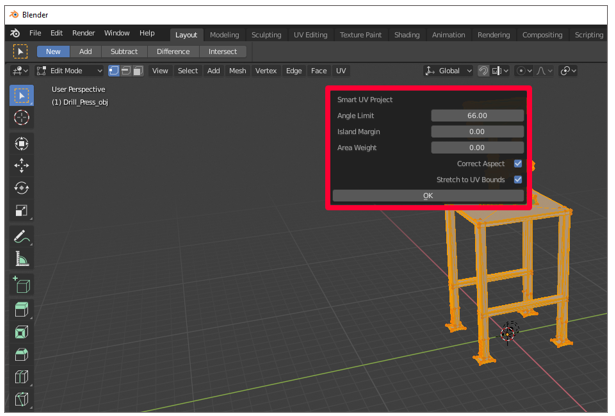
Keep the default settings for the backdrop, and then select OK.
-
Make sure that yous're in Edit Manner (press the Tab key), and that the unabridged model is still selected (press a). When the entire model is selected, it's orange.
-
Select the UV Editor menu (or press Shift+F10).

-
On the UV menu, select Pack Islands.
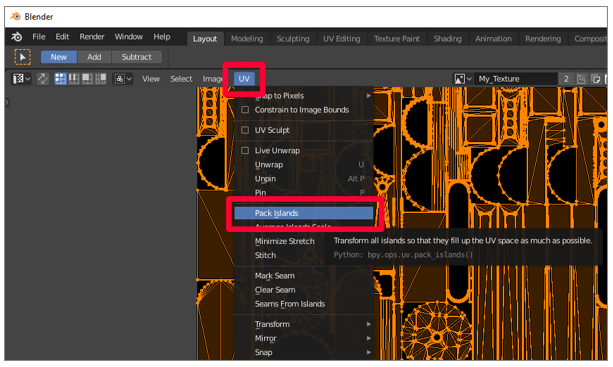
The outlined pieces are reorganized to correspond the surface of the model as efficiently as possible. Afterward packing the islands, the UVs await like this:
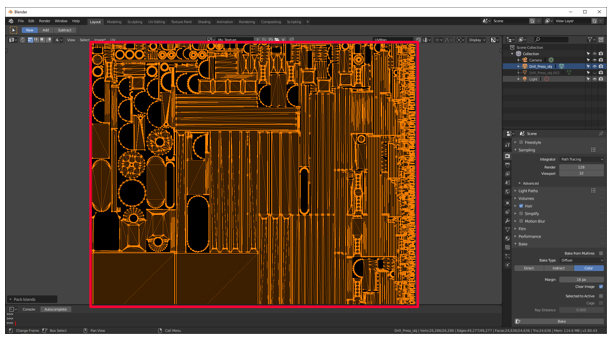
-
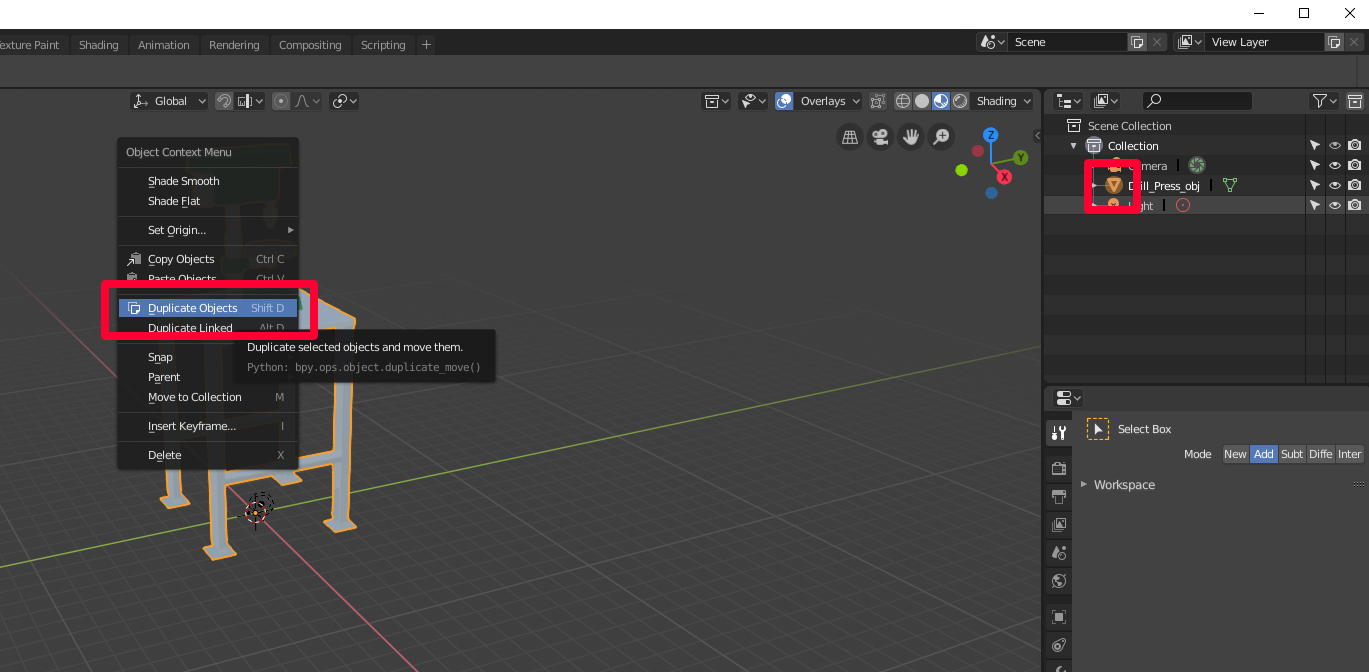
Create a copy of the mesh to bake the texture onto. To practice this:
a. Select the model.
b. Right-click the model to open the menu.
c. Select Duplicate Objects.
d. Press Spacebar.
Prepare materials for texture blistering
-
Select the duplicate model, and then select the Materials tab
 to become the Materials console.
to become the Materials console.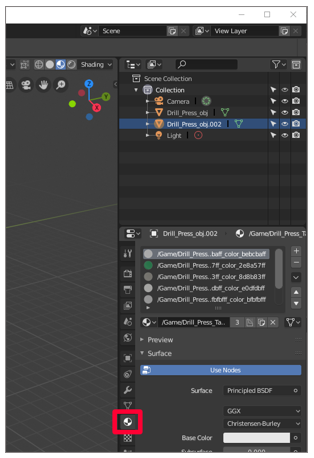
-
Delete all the materials for the duplicate 3D model by selecting the minus sign to the right of the materials.
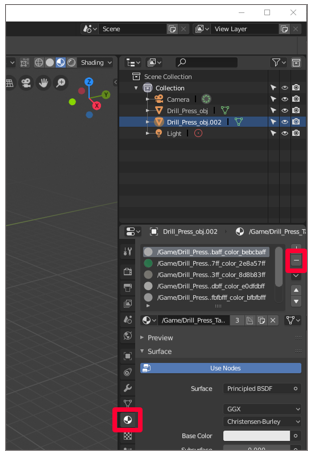
-
To hibernate the original 3D model and show merely the duplicate, select the "eye" to the right of the original 3D model name. Detect that there are no materials on the indistinguishable 3D model.
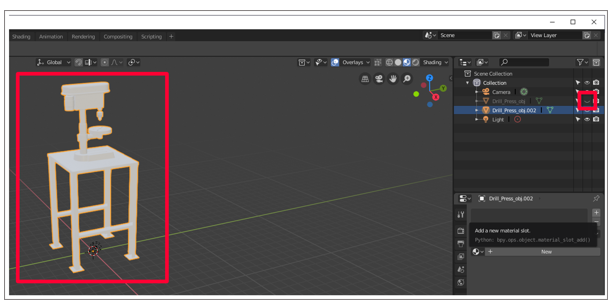
-
Select the plus sign in the Materials panel to add a new material to the duplicate.
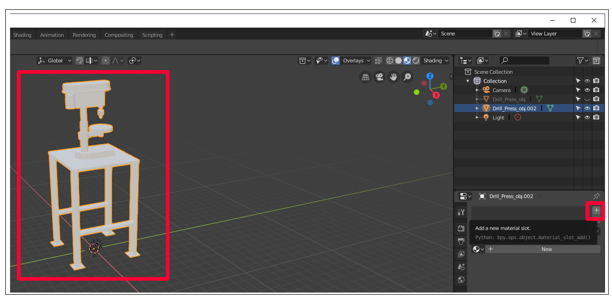
-
Select New to add a new material to the textile slot.
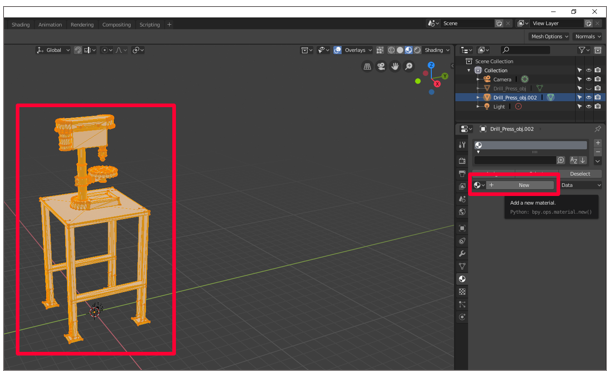
-
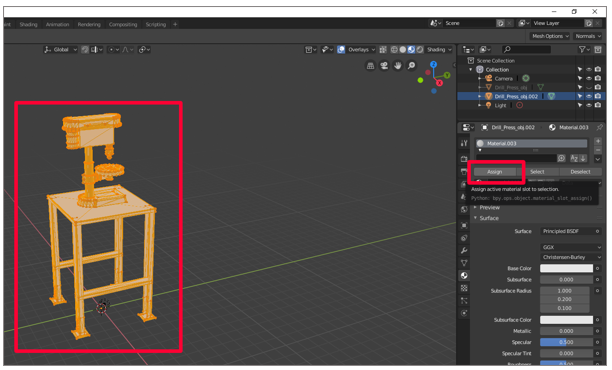
Hover over the viewport (the main window where the 3D model is shown), press the Tab fundamental to enter Edit Style, press a to select all, and so select Assign from the Materials tab
 .
.
-
Select the icon to the left of Object Mode, and so select Image Editor.
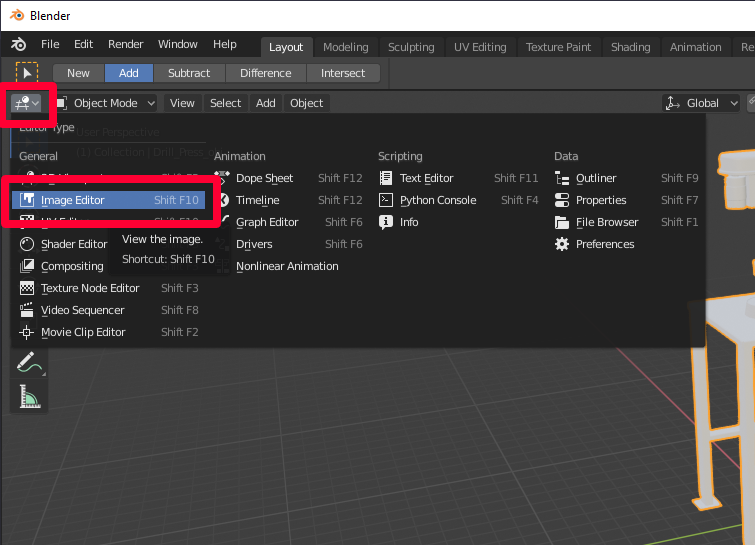
-
Create a new image (select Add > Epitome > New).
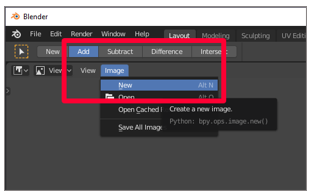
-
Save the new epitome every bit My_Texture or a similar proper noun that'south easy to remember, and then set the width and top to 1024 × 1024 pixels. Proceed the default values for the other options.
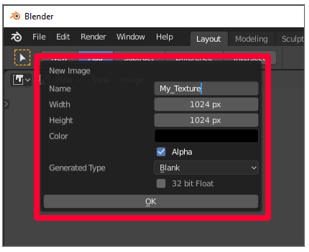
-
Select the icon to the left of View, and then select the Shader Editor.
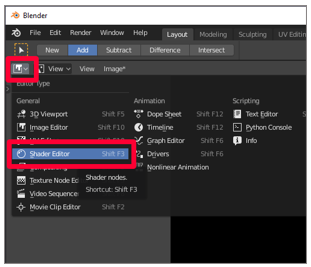
-
With the duplicate 3D model selected, select Add > Texture > Paradigm Texture. Select or click to place the image texture node in the window.
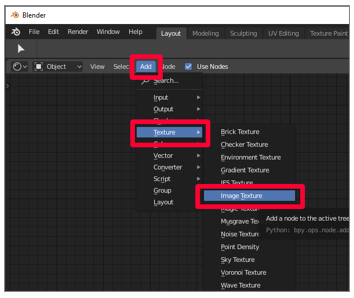
-
Drag the xanthous node link (the xanthous dot) labeled Color in the image texture window to the Base Color xanthous node on the Principled BSDF node, to connect them.
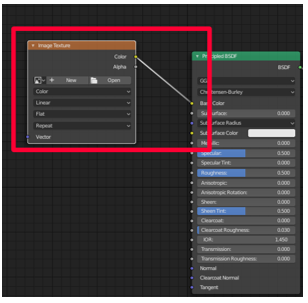
-
In the driblet-down menu on the prototype texture node, detect the texture you just created and select it.
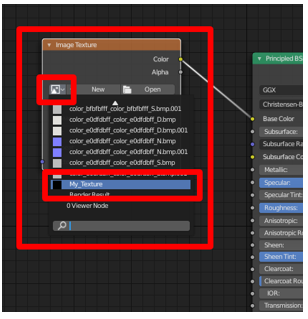
-
Select 3D Viewport at the upper left to get to the 3D Viewport menu.
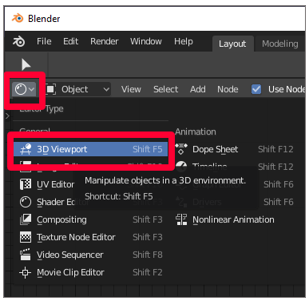
Bake the materials onto the texture
After the texture and material are set up on the duplicate 3D model, it'south fourth dimension to broil the materials from the original 3D model onto that texture. The texture volition be wrapped around the duplicate 3D model, which makes it higher performing while using the original colors.
-
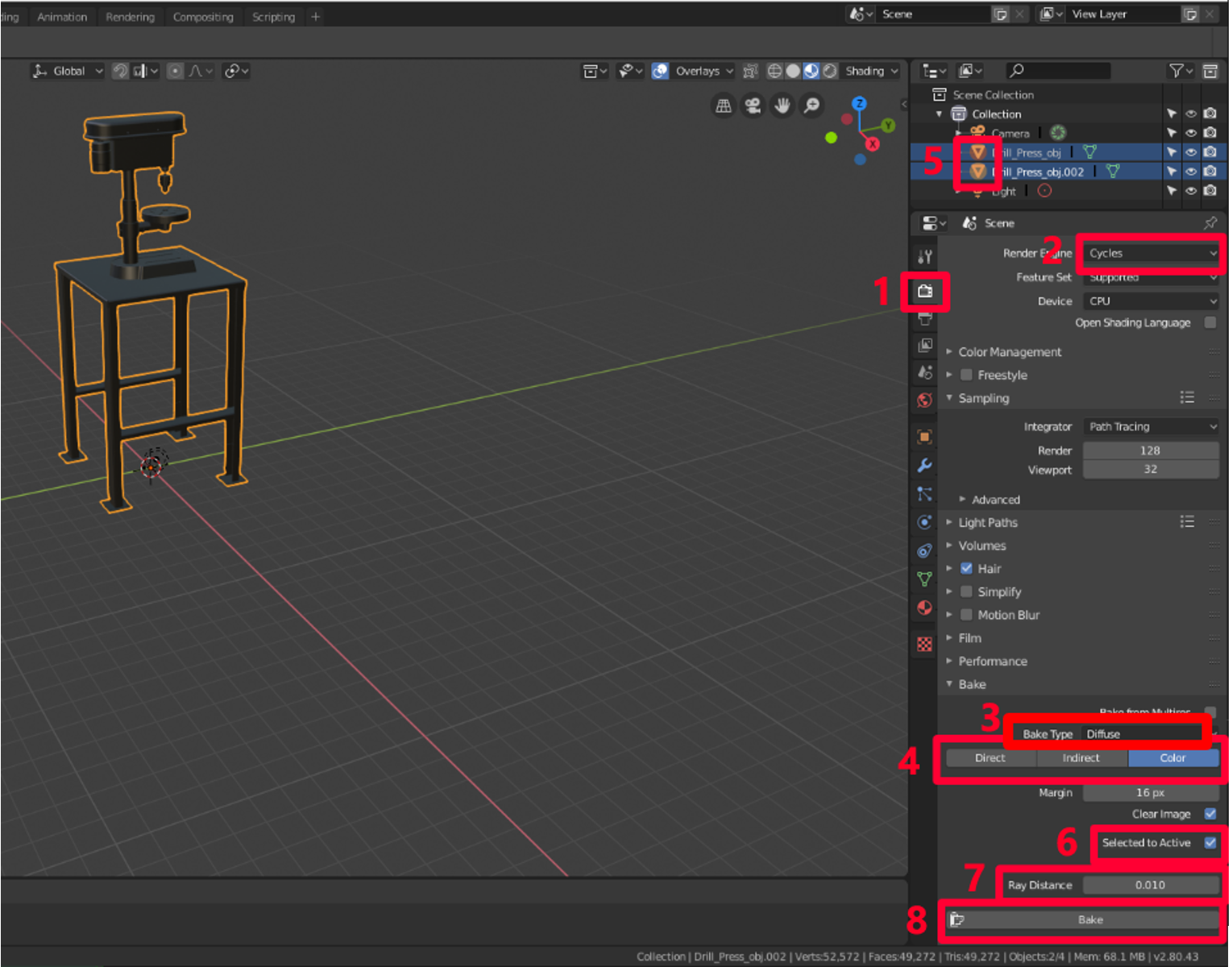
Select the Return tab

-
Select Cycles equally the render engine.
-
In the Bake menu, prepare Broil Blazon to Diffuse.
-
Clear the Direct and Indirect check boxes.
-
Select the original 3D model, and then hold Shift while selecting the duplicate 3D model.
-
Select the Selected to Agile check box.
-
Add a Ray Altitude value. Offset with .01, and and so increase it if the upshot is missing patches of color.
-
Select Broil.
The duplicate 3D model now has the same coloring equally the original, but with only one material instead of several. This can significantly reduce draw calls and increment performance.
To ostend that the bake was successful, you can select the eye icon
 adjacent to the original model to hide it. At present only the duplicate with one material and texture is visible.
adjacent to the original model to hide it. At present only the duplicate with one material and texture is visible.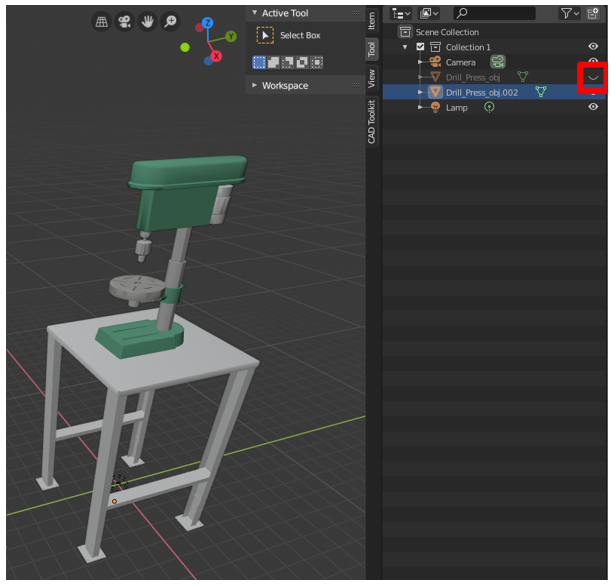
Export the model to a GLB file
The last stride is to export the model to a GLB file so it tin exist used with Dynamics 365 Guides and Power Apps.
-
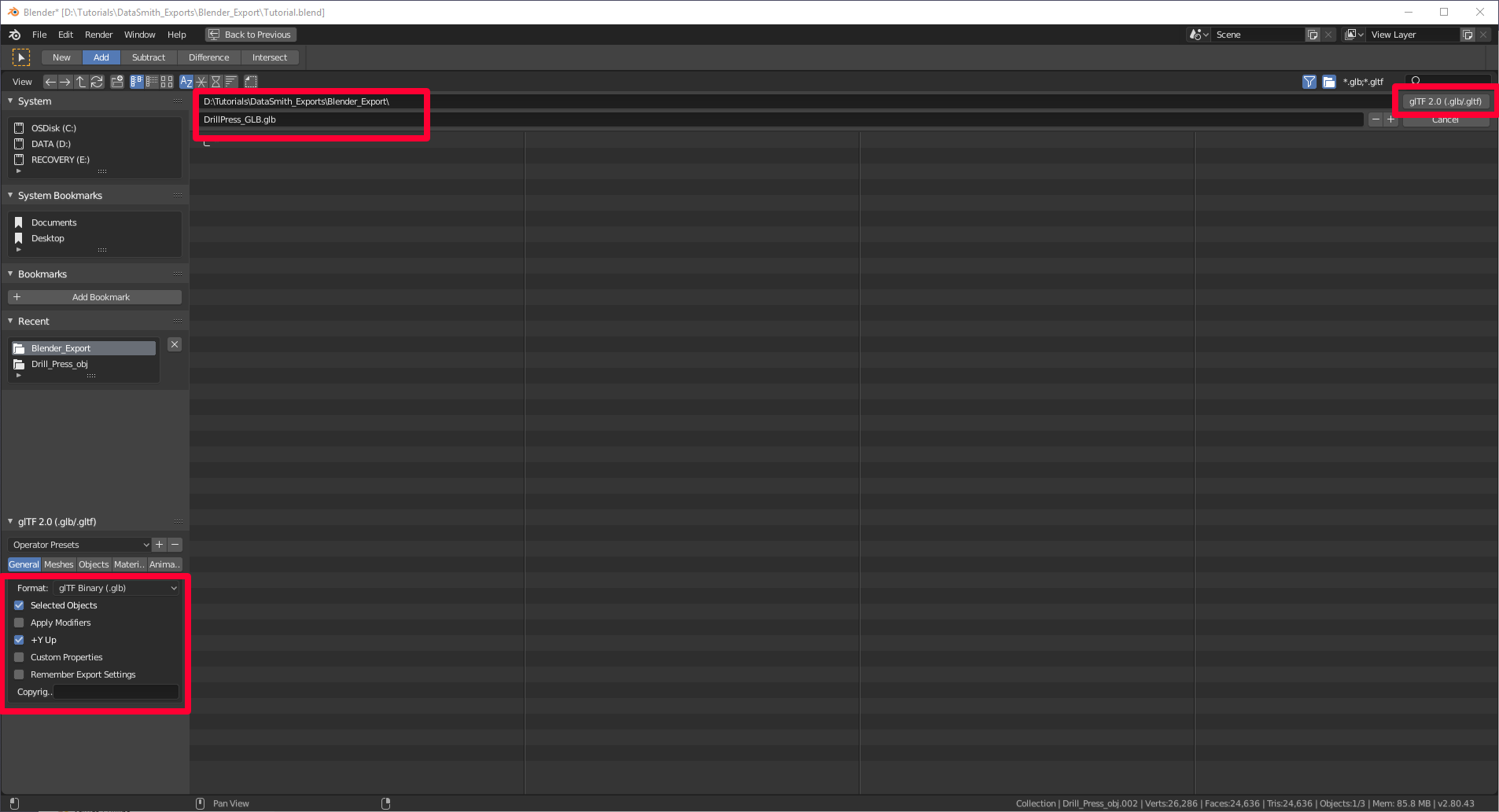
In Blender, select File > Export > glTF 2.0.
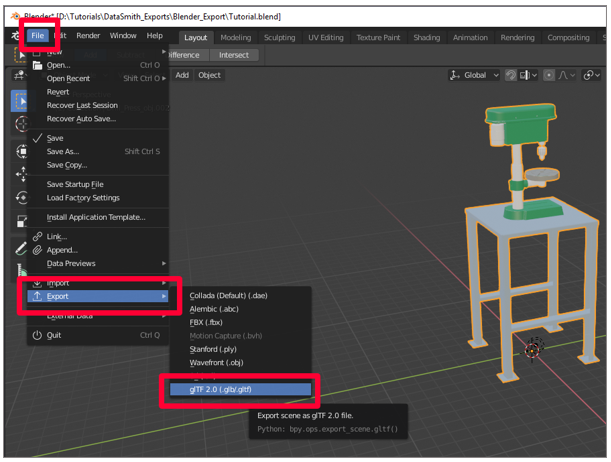
-
On the Export carte, make sure that the GLB format is selected and that the Selected Objects check box is selected. Name your file, and then select glTF 2.0 (.glb/.gltf).
View a 3D model in Dynamics 365 Guides or Power Apps
After you've prepared a 3D model, use the following links to learn more about using the model in Dynamics 365 Guides or Power Apps:
-
Dynamics 365 Guides
-
Power Apps
More than information
Several screenshots in this document were taken from the Blender software program in society to provide clear instructions on how to apply Blender's software. Larn more than nearly the Blender Foundation.
Microsoft Corporation is non responsible for, and expressly disclaims all liability for damages of whatever kind arising out of the employ of Blender, or reliance on these instructions. This document is created only to provide general information to our customers and does non take into consideration whatsoever individualized business organisation plans or specifications. Read about license terms for Blender at: Artistic Eatables Attribution ShareAlike.
The employ in this document of trademarked names and images is strictly for informative and descriptive purposes, and no commercial claim to their use, or suggestion of sponsorship or endorsement, is fabricated past Microsoft.
Feedback
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamics365/mixed-reality/guides/3d-content-guidelines/blender
Posted by: floresanion1954.blogspot.com


0 Response to "how to make a 3d model"
Post a Comment